Africa is the second-largest continent after Asia, The story of Africa’s physical geography begins 300 million years ago with the landmass known as Pangaea, the last supercontinent. Africa’s other major river, the Nile, flows from Lake Victoria in the rift valley north through 11 different countries. It is regarded by most as the longest river in the world. The Nile has, historically and in modern times, been a key way to transport people and goods throughout the region and its floodplain enables farming in an otherwise arid environment. Early humans were primarily gatherers, and there is evidence of people gathering nuts, grasses, and tubers around 16,000 BCE in the highlands of Northern Ethiopia. Around 10,000 years ago,
In Europe, colonial empires sought to expand their holdings to gain mineral resources and expand agricultural production. As Europeans began exploring the interior of Africa and recognized its resource potential, competition among European empires grew fierce. European colonization of Africa completely reshaped the political and ethnic landscape, with lasting effects even today.
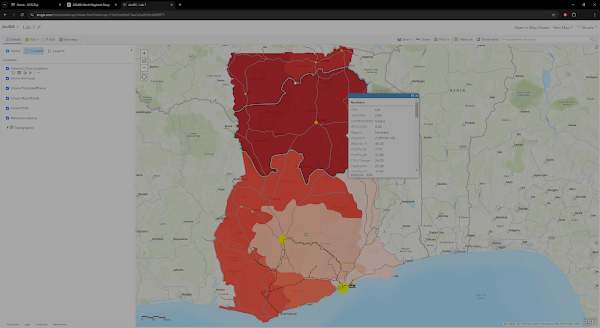
Today, Sub-Saharan Africa comprises 48 independent countries and is home to 800 million people. While colonialism transformed African politics and economics, the way of life for many Africans has changed relatively little. Sub-Saharan Africa’s population has been climbing rapidly with the highest fertility rates of any region in the world



No comments:
Post a Comment